Long distance sensors: measuring large distances (more than 10 meter)
Ultrasonic sensors
An ultrasonic sensor emits a sound wave and then waits for the reflection or echo. The time of flight is used to calculate the distance. Distances of a few meters are within its range. This page contains more information on applications for ultrasonic sensors and how they work.
Lidar sensor
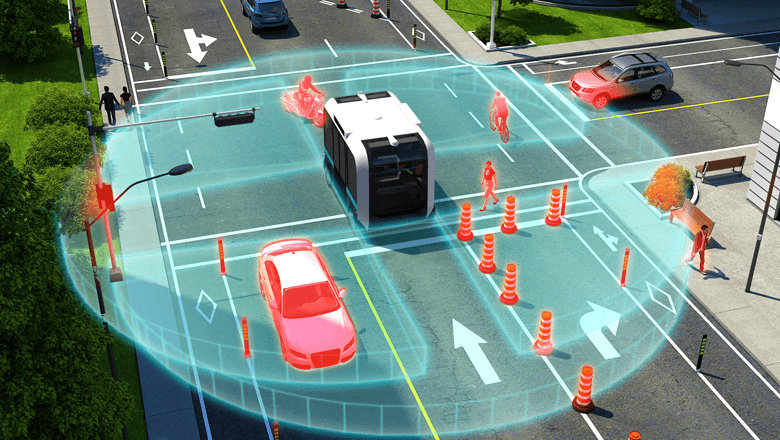
Lidar, which stands for ‘light detection and ranging’, works like a laser sensor with light pulses and the time-of-flight principle. The difference is that a lidar scans the environment. The result is a 3D point cloud that contains a lot more information than the single-point measurement produced by a laser sensor. Lidar systems are widely used in AGVs, AMRs and autonomous vehicles. They are also suitable for tasks such as crowd management at airports to map out crowds, or monitoring railway crossings in the dark when normal cameras fail.
Which lidar is best for your application?
Two types of lidar sensors are available. The first type is a revolving system with a 360° viewing angle. That produces an excellent image, but you do have to be able to fit it into the design of your product. It is rarely the best solution for agricultural applications as the vibrations can damage the mechanism, for example. The second version, which is now quickly growing in popularity, is the solid-state lidar. These chips have no moving parts, which guarantees a long service life. They do have a limited viewing angle, however, typically between 70° and 90°.
Radar sensors
A third possibility for measuring long distances is radar technology. It is comparable to a rotating lidar, but uses radio waves. In theory, this also works over shorter distances, but the accuracy in such circumstances is limited. Radar sensors are also traditionally quite expensive, which has made them too costly for most industrial applications.
However, modern radar modules are getting cheaper, and are even available in chip form. The range may be limited, but they are a serious alternative for multiple applications. The radio waves of a radar module can pass through plastic, so they can be safely enclosed and used in aggressive or rough environments.
Speed measurements
The advantage of lidar and radar is that they are not limited to measuring distances, but can also be used to measure speeds and locate objects within the viewing angle by comparing two consecutive measurements. In terms of cost, there is very little difference between the two methods. They are often used in combination. Radar can detect further ahead, and is insensitive to factors such as fog, while lidar provides detailed images. A self-driving car needs both signals.
Featured long distance sensors
Need some help?
Our sensor database only lists a selection of the sensors available. There are so many different technologies and manufacturers that our online sensor database can never be 100% complete. If you can’t find what you’re looking for, or you have a question, send an e-mail to our sensor experts. We’ll gladly help you with your search.